Itchy Rash in Adults: Causes, Treatments, and When to See a Doctor
Itchy rashes in adults are a common skin condition that can cause discomfort, affect appearance, and significantly reduce quality of life. This condition may result from various causes such as allergies, skin infections, autoimmune diseases, or psychological factors. Understanding the causes and proper treatment methods can help manage symptoms effectively and prevent recurrence.

What Is an Itchy Rash in Adults?
An itchy rash is a skin condition characterized by red spots, patches, or bumps accompanied by itching that can range from mild to severe. The rash may appear in a localized area or spread across the body, lasting for a short period or becoming chronic if not treated properly.
Causes of Itchy Rashes in Adults
Allergies
Allergies are one of the most common causes of itchy rashes in adults. When the body comes into contact with an allergen, the immune system releases histamine, leading to itching and skin eruptions.
Common allergens include:
-
Food allergies: Seafood, milk, eggs, peanuts, and tree nuts.
-
Drug allergies: Antibiotics such as penicillin and sulfonamides.
-
Environmental allergens: Pollen, household dust, pet dander, and mold.
Contact Dermatitis

Contact dermatitis occurs when the skin comes into direct contact with irritating or allergenic substances.
Common triggers include:
-
Chemicals found in soaps, cosmetics, and cleaning products.
-
Metals such as nickel, often present in jewelry.
-
Certain plants, including poison ivy and poison oak.
Skin Infections
Skin infections caused by bacteria, fungi, or viruses can also lead to itchy rashes, often accompanied by redness, pain, or scaling:
-
Fungal infections: Athlete’s foot, ringworm, or nail fungus.
-
Shingles: Caused by the varicella-zoster virus, often associated with pain and itching.
-
Staphylococcal infections: Can cause boils, inflamed lesions, and itching.
Autoimmune Diseases
Some autoimmune conditions can manifest with persistent itchy rashes:
-
Lupus erythematosus: Causes red patches and photosensitive skin.
-
Atopic dermatitis (eczema): A chronic condition marked by dry, itchy, inflamed skin.
-
Psoriasis: Characterized by thick, red patches covered with silvery scales and itching.
Psychological Factors
Stress, anxiety, and other psychological issues can worsen itching. When stressed, the body releases inflammatory substances that make the skin more sensitive and prone to irritation.
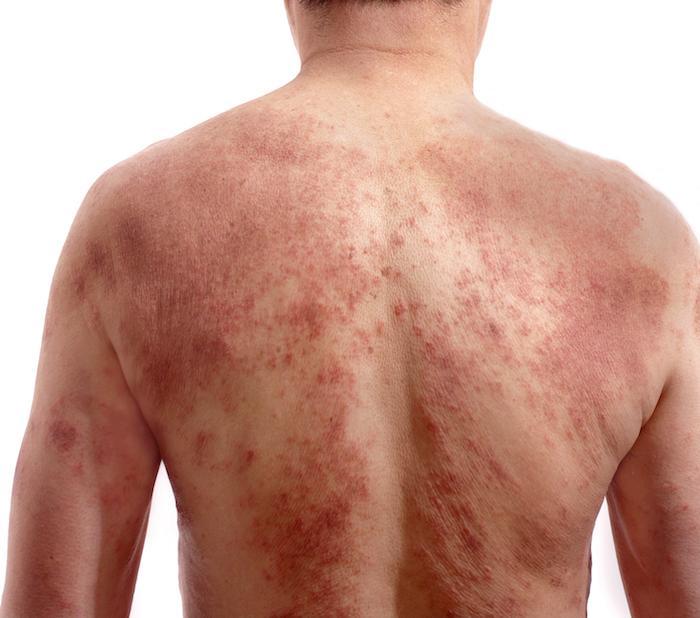
How to Treat Itchy Rashes in Adults
Over-the-Counter Medications
-
Antihistamines: Medications such as cetirizine, loratadine, and diphenhydramine help reduce itching caused by allergies.
-
Topical corticosteroids: Creams containing hydrocortisone can help reduce inflammation and itching when applied directly to the affected area.
Lifestyle and Daily Habit Changes
-
Avoid known allergens and skin irritants.
-
Maintain good personal hygiene and a clean living environment.
-
Use gentle, fragrance-free skincare products suitable for sensitive skin.
-
Wear loose-fitting clothing made from breathable fabrics.
Natural Remedies
-
Aloe vera gel: Soothes the skin and reduces inflammation.
-
Coconut oil: Provides moisture and has mild antibacterial properties.
-
Oatmeal or baking soda baths: Help relieve itching and calm irritated skin.
Treating Underlying Conditions
If itchy rashes are caused by underlying conditions such as lupus, eczema, or psoriasis, treating the root disease under medical supervision is essential for long-term symptom control.
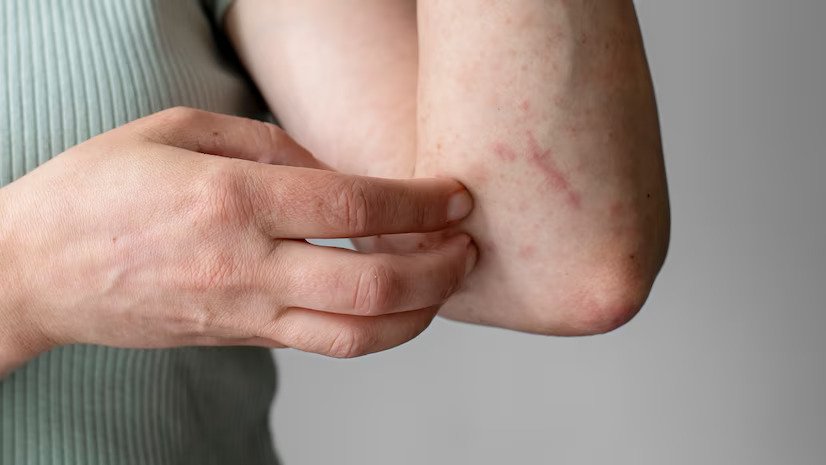
When Should You See a Doctor?
You should seek medical attention if:
-
The rash does not improve after self-care or over-the-counter treatment.
-
The rash spreads rapidly or shows signs of infection such as swelling, redness, or pus.
-
Additional symptoms appear, including fever, difficulty breathing, or chest pain.
-
Persistent itching interferes with sleep and daily activities.

Conclusion
Itchy rashes in adults can result from a wide range of causes, from simple allergies to complex autoimmune diseases. Identifying the correct cause and applying appropriate treatments can significantly relieve symptoms and improve quality of life. In cases where the rash is severe, persistent, or of unknown origin, consulting a dermatologist is the best way to ensure effective and safe treatment.