Drooling while sleeping is a common phenomenon that affects both adults and children. Many people feel embarrassed or concerned, assuming it signals a health problem. In reality, drooling during sleep is often harmless and can even indicate that your body is entering a deep state of rest. So when is it normal, and when should you be concerned? Let’s explore the details.
Drooling During Sleep as a Sign of Deep Relaxation
One of the most common reasons for drooling while sleeping is deep, restorative sleep. During deep sleep stages—especially REM sleep—your muscles fully relax, including the muscles that control the jaw and swallowing reflex.
When swallowing slows down compared to waking hours, saliva can build up and escape from the mouth. In this sense, drooling may actually be a sign of good sleep quality.
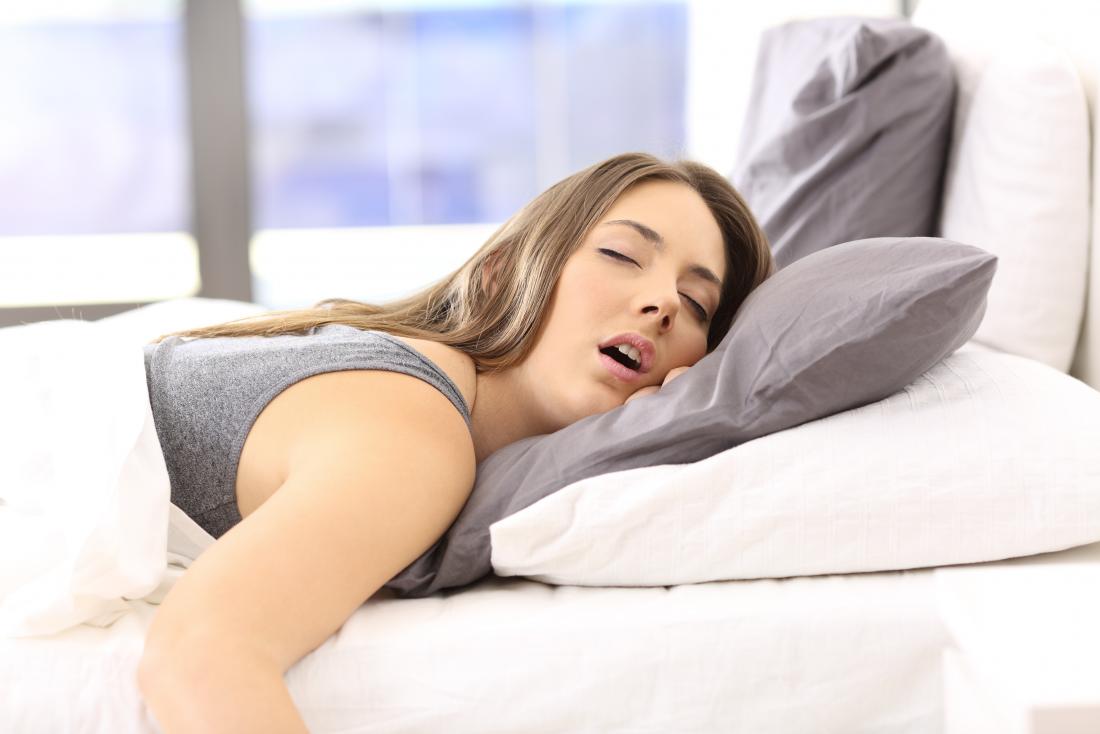

Sleep Position Plays a Major Role
Your sleeping position has a significant impact on whether you drool at night. People who sleep on their side or stomach are more likely to drool because gravity allows saliva to flow out of the mouth.
Those who sleep on their backs tend to drool less, as saliva naturally stays in the mouth and is swallowed more easily. Adjusting your sleep position can noticeably reduce this issue.

Nasal Congestion and Mouth Breathing
When nasal passages are blocked due to colds, allergies, or sinus problems, the body often switches to mouth breathing during sleep. This causes the mouth to remain open for long periods, increasing the likelihood of drooling.
Individuals with chronic sinus issues or a deviated septum are particularly prone to this condition.
Excessive Saliva Production
Some people naturally produce more saliva than others. Certain medications, including those used for allergies, depression, or neurological conditions, may increase saliva production as a side effect.
Digestive issues such as acid reflux or GERD can also stimulate excessive saliva production, especially at night.
Neurological and Muscle Control Factors
In less common cases, frequent drooling during sleep may be linked to neurological conditions or reduced muscle control. Disorders such as sleep apnea, Parkinson’s disease, stroke, or other neurological issues can interfere with the swallowing reflex.
Sleep apnea, in particular, can cause mouth breathing and disrupted sleep, making drooling more likely while also posing broader health risks.
When Should You Be Concerned About Drooling While Sleeping?
Occasional drooling is usually harmless. However, medical attention may be necessary if it:
-
Occurs frequently or worsens over time
-
Is accompanied by difficulty swallowing, loud snoring, or interrupted sleep
-
Appears suddenly without an obvious cause
These signs may point to an underlying condition that requires evaluation.
How to Reduce Drooling While Sleeping
If drooling affects your comfort or sleep quality, consider the following solutions:
-
Adjust your sleep position and try sleeping on your back
-
Treat nasal congestion with saline sprays or a humidifier
-
Stay well hydrated to prevent thick saliva
-
Review medications with your doctor if saliva production increases
-
Seek evaluation for sleep apnea or acid reflux if symptoms persist

Conclusion
Drooling while sleeping is usually a normal and harmless condition linked to deep sleep, sleep posture, or mouth breathing. However, persistent or excessive drooling—especially when paired with other symptoms—should not be ignored.
Paying attention to your body and seeking medical advice when necessary can help protect both your sleep quality and overall health.